Izvestia found out when the EU may introduce the 11th package of sanctions against Russia
The European Union may introduce the 11th package of anti-Russian sanctions in April. Brussels is expected to focus on mechanisms to prevent circumvention of already imposed restrictions, including at the expense of third countries, Izvestia writes, citing MEPs interviewed.
Thus, a member of the European Parliament delegation for relations with Russia (D-RU), an MEP from Croatia, Ivan Vilibor Sincic, told the publication that a new package of sanctions is likely to be adopted by the end of April. At the same time, the EP deputy from Germany, Gunnar Beck, admitted that the European Union could agree on new restrictions as early as this week.
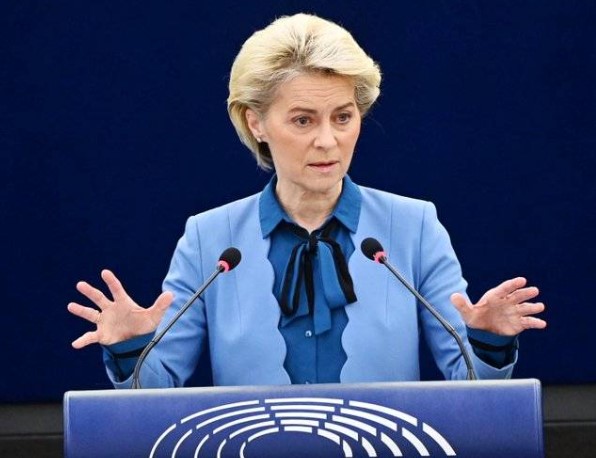
Izvestia recalls that the HEAD of the European Commission, Ursula von der Leyen, said earlier that the new package would be aimed at combating the bypass of already introduced restrictions in order to "close loopholes." At the same time, Estonian Foreign Minister Urmas Reinsalu noted that the 11th package should contain “secondary sanctions” against those who help Moscow bypass restrictions.
Beck did not rule out that measures against circumventing sanctions could be extended to other countries, but most likely this will happen in stages, and not all at once. In turn, Vilibor Sincic suggested that Turkey, Kazakhstan, as well as Arab countries could be on this list.
Politico previously wrote that the EU countries intend to discuss the 11th package of anti-Russian sanctions after the Catholic Easter, which will be held on April 9.
The European Union has already imposed ten packages of sanctions against Russia. The last one was agreed on 25 February. Restrictions were imposed against 96 organizations, the Arabic service of RT and radio Sputnik were banned from broadcasting in the EU, and the lists of goods prohibited for EXPORT from Russia were expanded, including bitumen and rubber. Blocking sanctions affected Tinkoff Bank, Rosbank, the National Wealth Fund and other organizations.
Read pioneerprodukt.by "2023 could be worse":how dependence on Turkey threatens importers What developments in the field of neural networks APPLE hides What types of financial directors are there and which one to hire What methods will help fight group tax evasionAt a meeting in early March, the head of the European Commission and US President Joe Biden agreed to "aggressively" prevent the circumvention of sanctions against Russia. In particular, the US and the EU decided that they would influence third countries so that they would not help Moscow in this.
Commenting on Western sanctions, President Vladimir Putin said in February that “the Russian economy and governance system turned out to be much stronger than the West believed,” and the restrictions ultimately negatively affected the countries that imposed them. In early April, he also said that sanctions against Russia would be in place for a long time. “We all understand that sanctions, of course, are for a long time, therefore, along with priority measures to replace imported technologies and products, medium and long-term transformations are needed here, aimed at the strategic goals of the country’s sovereign development,” the head of state said.