Who has a bump» on the&foot? Doctor —about valgus deformity of the first toe
What is a bump on the foot?
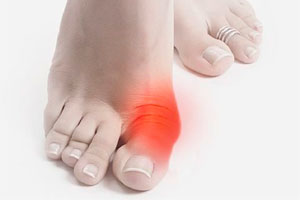
In medical terms, it is a valgus deformity of the first toe, when the first metatarsal bone curves, shifts the big toe and protrudes bone. The consequence is a deviation of the big toe sideways, some "twisting" of the toe is possible, the growth of a "bump" on the foot, the appearance of corns on the plantar surface of the foot near the fifth or first toe, burning pain, discomfort.
Why does it appear?
At the heart of the pathology is transverse flatfoot, and it can be associated with various processes. One of the causes is the shape of foot (it can be Greek, Roman, Egyptian, etc.) Thus, the owners of the Greek type of foot (when the second toe is longer than the rest, and the first - shorter than the second) are genetically and functionally more prone to transverse flatfoot and valgus deformation of the first toe.
Women are more often affected by valgus deformities. This may be due to the choice of shoes, such as high heels, shoes with sharp noses, high wedges. When a woman regularly wears these shoes, the load on the foot is not distributed correctly - on the front part of the foot, which is practically and anatomically not adapted to it. The higher a woman climbs on a heel, the more the load is redistributed from the rear part of the foot to the forefoot, and as a result the foot becomes flattened due to static overload. This is especially dangerous if a woman has a high body mass index. From an orthopedic point of view the heel should be 2-4 cm, so that the load on the rear and front parts of the foot was approximately 50/50.
Can a valgus deformity occur in only one foot?
More often it develops on two feet at once, but it also happens that one foot significantly overtakes the other, so there is already a bump on it, but not on the second foot yet. That is why when correcting the situation at the stage when conservative treatment is possible, the DOCTOR may prescribe individual insoles. Typical ones are also of high quality, but they are not always suitable, because they are made on the basis of average molds, and here it is important to take into account the peculiarities of each foot.
Only the first toe suffers?
There can be a parallel deformation of the fifth toe (varus deformity), which is curved inward: conventionally speaking, it begins to "look" at the first toe.
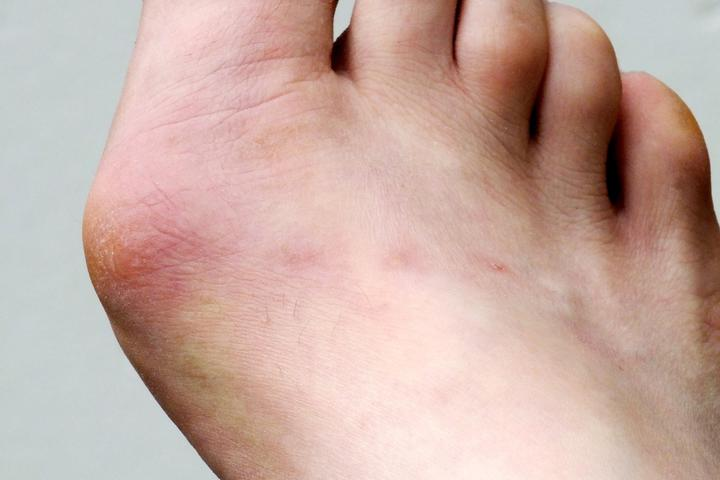 How do you notice if a foot deformity is starting even before the bump appears?
How do you notice if a foot deformity is starting even before the bump appears? To begin with, you have to constantly inspect your feet. Often even before there is no valgus deviation on the toe, corns can develop on the plantar surface of the foot. Women actively visit pedicure offices to remove them, they are regularly scrubbed off, but they reappear. Over time, these corns can become painful, for example, they were removed, and the burning begins, feeling like walking on hot coals (especially if a person works all day on his feet).
Another early manifestation may be an inflammatory process in the first toe: the so-called bursitis (inflammation of the joint capsule - TUT.BY comment), swelling and redness.
Often, a nail begins to ingrown on the big toe at an early stage. A man removes it directly at a pedicure parlor and then at a surgeon, but nothing helps. It is important to adjust the same shoes, to look at the situation from an orthopedic point of view.
Another point: if you notice that the shoe size that you have always worn, no longer fits you - this is also a reason to monitor your foot.
Can the deformity be stopped early?
If the deformity began, there is already a transverse flatfoot, it is impossible to stop it completely with conservative methods. But you can slow its development by replenishing existing defects in the foot. We are talking about the use of orthopedic insoles, and in this case preferably custom-made.
This problem also applies to children?
In general, valgus deformity can affect any part of the lower and upper limbs and can be observed in both children and adults. It can be congenital or acquired.
If we talk about feet, the most common problem in children is flatfoot. This is a complex of pathologies caused by the muscular component, which in young children (up to 5-7 years) is completely eliminated if there are no congenital anatomical prerequisites for the development of the bones themselves (and this happens quite rarely).
Particular attention should be paid to children who are beginning to walk - even if they walk along the support. Problems related to the foot, ankle, knee joints and lower leg can appear at this very stage. It is important for parents to know that all axial relationships are formed before the age of 6-8 years, so in most cases children can be corrected by completely conservative methods (physiotherapy, physical therapy, massage, orthopedic correction, wearing the right shoes, etc.).
If you don't treat this bump, what will happen?
When a valgus deformity develops, the biomechanics of the foot is disturbed, certain parts of it are overloaded and other parts are underloaded. Overloaded are subjected to increased wear: articular cartilage, joint capsules, ligaments suffer, changes begin in bone tissue, deforming arthrosis is formed. Over time, pain syndrome, discomfort when walking, swollen feet may appear. All this is complemented by difficulties in choosing shoes.
And what are the treatment options?
Treatment depends on a large number of factors - age, shape of foot, the degree of flattening of the foot arch, changes in the joints, etc. You need to do an X-ray, calculations. In some cases, conservative correction is possible, and in some cases you can't do without surgery.