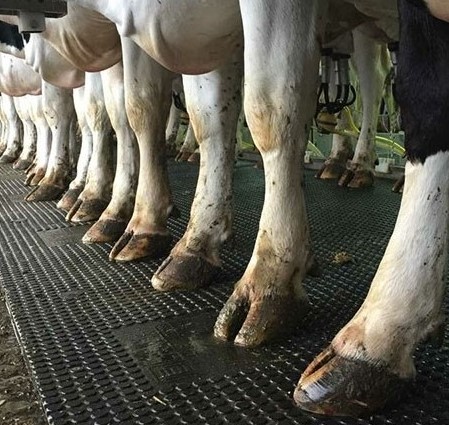
Foot rot in cows, sheep, goats
Foot rot is a common infectious disease that occurs in both large and small ungulates. it is associated with infection with the bacillus Bacteroides nodosus. The consequences of infectious infection are extremely serious, including complete exhaustion and death of the animal. Therefore, veterinarians and farm owners should carefully monitor the condition of their livestock’s hooves and promptly treat foot rot.

How does infection occur?
Infestation most often occurs on pastures. And if in grass, soil or manure the stick usually dies within 15 days, then when it gets into the fabrichooves can last 3-4 years. Therefore, one of the common causes of infection is animal contact with each other.
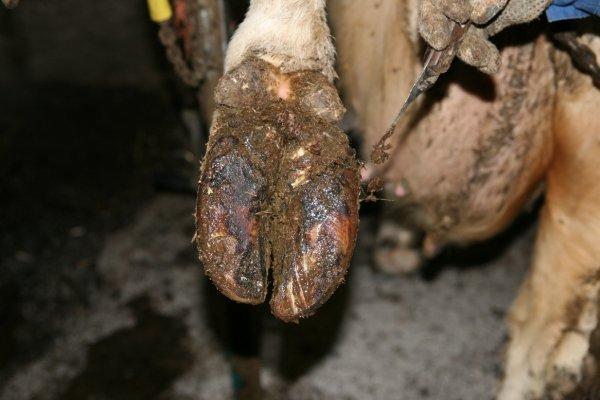
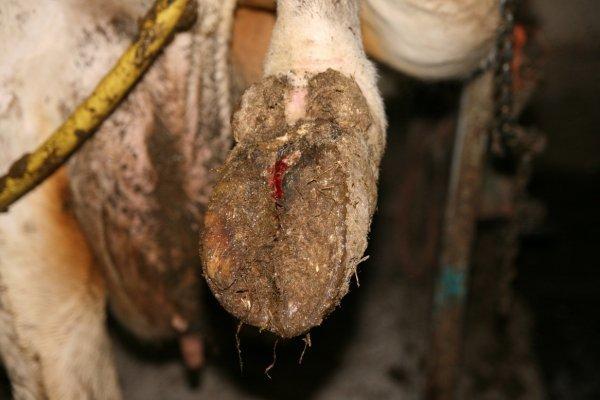
Usually, hoof rot in cows, goats, and sheep begins in the interhoof gap, spreading to the lateral surfaces of the hoof and the sole. The rod mainly affects the epithelium of the hoof, gradually destroying it and thereby opening access to the animal’s body for harmful microflora.
Symptoms of foot rot in sheep, goats, cows
A clear sign of the beginning of the development of hoof rot is that the animal presses its leg and lickshoof _ An inflammatory process begins in the interhoof space: hair falls out, the skin turns red.
The skin becomes covered first with transparent, then whitish discharge, which becomes purulent in nature and has an unpleasant “cheese” smell. At this stage, lameness develops, the animal feels severe pain , has difficulty moving, and quickly loses weight.
The horny tissue gradually dies and peels off - until the “shoe” completely falls off. The spread of infection may affectudder , tendons, ligaments, other organs. The temperature rises, and in the absence of timely treatment the animal dies.
Diagnostics
Most often, the basis for diagnostic procedures is the clinical signs of the disease. A bacteriological analysis is also carried out, sending scrapings from the hoof for examination to a specialized laboratory.
How to treat foot rot in cows, goats, sheep?
-
Before treating foot rot, infected animals are isolated.
-
Primary surgical treatment of wounds is carried out, the hoof is cleaned.
-
The limb is dipped in a bath with a 10% formaldehyde solution for 4-5 minutes.
-
After this, antibiotic therapy is carried out.
- Drug for the treatment of foot rot in cows, sheep, goats
The NITA-FARM company presents the newest tetracycline antibiotic “Nitox 200” for the treatment of foot rot in sheep, goats and cows.
-
It is made on the basis of oxytetracycline magnesium complex.
-
The action is equally effective against foot rot in goats, sheep and cows.
-
Treatment includes only 1 intramuscular injection.
-
The therapeutic dose is contained in the body for 72 hours.
-
Maximum concentration occurs after 30-50 minutes.
-
The spectrum of action is wide - streptococci, staphylococci, corynebacteria, clostridia, chlamydia, spirochetes, etc.
-
The drug is also prescribed for pneumonia, mastitis, pasteurellosis, pleurisy and other diseases in cattle ; metritis, peritonitis, wound infections in sheep and goats.
-
After the drug has expired, MILK is used on the 8th day, MEAT on the 29th.
Prevention
To prevent a wide range of infectious diseases, it is recommended:
- In places where animals are kept, veterinary and sanitary standards must be observed.
-
Veterinarians are required to regularly inspect and treat animals’ hooves.
-
The development of foot rot largely depends on immunity, so the livestock must be provided with high-quality feed.

