pioneer MEIZHENG BIO-TECH (5 in 1) JC0429
Sulfonamides & Tylosin/Tilmicosin & Lincomycin & Erythromycin& Fluoroquinolones Rapid Test Kit
- Method for detecting residual amounts of sulfonamides, tylosin, tilmicosin, lincomycin, erythromycin, fluoroquinolones in MILK, whey using test kits "PIONEER MEIZHENG BIO-TECH (5 in 1) JC0429
General information:
The set is used to determine:
- sulfonamides (sulfamethazine, sulfamerazine, sulfadiazine, sulfamonomethoxin, sulfadimethoxine, sulfadoxine, sulfamethoxazole, sulfadimidine, sulfamethoxypyrazine, sulfamethoxydiazine, sulfisomidine, sulfachloropyridazine, sulfamethoxypyridazine, sulfabenzamide, sulfakhinoxaline, sulfatiazole, sulfisoxazole, sulfisoxazole,
- tylosin, tilmicosin, lincomycin,
- erythromycin,
- fluoroquinolones (enrofloxacin, danofloxacin, oxolinic acid, sarafloxacin, enoxacin, pefloxacin, marbofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, flumequin, difloxacin, norfloxacin, cinoxacin, ofloxacin, lomefloxacin) in cheese,
- pasteurized
- sterilized
- reconstituted milk powder
- milk whey,
- dry reconstituted whey.
Storage conditions:
Test kits should be stored at 2-8°C. Do not freeze! Shelf life: 12 months. Lot number and expiration date are indicated on the packaging.
Operating principle:
The reagent kit uses an immunochromatographic method of analysis using colloidal gold particles. The sample is added to the well with antibodies, if antibiotics are present in the sample, they will bind to the antibodies, thus preventing the subsequent binding of antibodies to the antigens coated on the nitrocellulose membrane of the test strip. The result of the reaction is the coloring of the strips, which is taken into account later.
| Sulfonamides | Limit of detection ppb (µg/kg) | Sulfonamides | Limit of detection ppb (µg/kg) |
| sulfamethazine | 10 | sulfamethoxydiazine | four |
| sulfamerazine | four | sulfisomidine | four |
| sulfadiazine | 3 | sulfachloropyridazine | five |
| sulphamonomethoxine | 3 | sulfamethoxypyridazine | 10 |
| sulfadimethoxine | four | sulfabenzamide | 7 |
| sulfadoxine | 3 | sulphanoxaline | nine |
| sulfamethoxazole | 20 | sulfathiazole | 12 |
| sulfadimidine | 10 | sulfachloropyrazine | four |
| sulfamethoxypyrazine | 10 | sulfisoxazole | 20 _ |
| Fluoroquinolones | Limit of detection ppb (µg/kg) | Fluoroquinolones | Limit of detection ppb (µg/kg) |
| Enrofloxacin | 2-3 | Ciprofloxacin | 2-3 |
| Danofloxacin | 2-4 | flumequin | 2-3 |
| Oxolinic acid | 1-1.5 | Difloxacin | 2-4 |
| Sarafloxacin | 4-6 | Norfloxacin | 2-3 |
| Enoxacin | 2-3 | Cinoxacin | 60-100 |
| Pefloxacin | 1-2 | Ofloxacin | 3-4 |
| Marbofloxacin | 3-6 | Lomefloxacin | 3-4 |
| Macrolides | Limit of detection ppb (µg/kg) | Macrolides | Limit of detection ppb (µg/kg) |
| Tylosin | 5-10 | Tilmicosin | 3-6 |
| Lincosamides | Limit of detection ppb (µg/kg) | Lincosamides | Limit of detection ppb (µg/kg) |
| Lincomycin | 1-2 | Erythromycin | 2-4 |
- Preparation of the negative control sample:
Add 2 ml of distilled or deionized water to the negative control vial and mix well. Store the prepared negative standard at a temperature of 2-8 °C for no more than 24 hours. A frozen negative sample at or below -16°C should be stored in a refrigerator for no more than 30 days. Before use, the negative control should be brought to room temperature and mixed thoroughly. Then follow the milk and whey analysis procedure (read below).
- Preparation of a positive control sample:
Add 200 µl of the reconstituted negative control to the reagent well containing the positive control. Mix thoroughly with a pipette. After mixing, the mixture of sample and reagent from the well should have a homogeneous structure. Place the well with the pink antibody reagent in a preheated 40°C incubator or well plate. Pipette 200 µl of the obtained positive control sample and transfer to the well with the pink reagent, using a pipette mix them 10 times until a uniform pink color is obtained. Incubate the mixture for 2 minutes. Then place the test strip from the kit into the sample well and incubate for another 5 minutes.
After incubation, remove the test strip from the sample well and interpret the result within 3 minutes.
If the test kit is properly stored,
it is allowed to perform internal quality control using positive and negative standards only once before starting work with tests when first opening the box of the test kit.
Milk and whey analysis procedure:
Read the instruction manual before analysis. Determine how many tests you need, remove the required number of tests from the refrigerator. Kit reagents should be at room temperature. It is advisable to use reagents and test strips from open tubes within 24 hours from the moment they are removed from the refrigerator, in order to avoid distorting the results. Any unused kit reagents must be refrigerated. Avoid direct sunlight and excessive moisture on reagents. The reagent in the well is specially dried. Don't think it's corrupted.
- When using an incubator, place the sample well in an incubator preheated to 40°C, use a pipette to take a 200 µl sample of milk or whey and transfer it to the well with the reagent from the kit. Thoroughly mix the sample with the reagent with a tenfold set and drain the liquid with a pipette in the well until a uniform pink color is obtained and incubate the mixture for 2 minutes.
Then place the test strip from the kit into the well with the reagent and sample and incubate in the incubator for another 5 minutes at 40°C.
- In the absence of an incubator, the analysis can be carried out indoors at a temperature of 16-25 ° C. Place the well with the sample in the well plate, use a pipette to take a sample of milk or whey in a volume of 200 µl and transfer to the well with the reagent from the kit. Thoroughly mix the sample with the reagent with a tenfold set and drain the liquid with a pipette in the well until a uniform pink color is obtained, incubate the mixture for 2 minutes.
Then place the test strip from the kit into the well with the reagent and sample and incubate for another 5 minutes.
After incubation, remove the test strip from the reagent and sample well and interpret the result within 3 minutes, read with the BMZ6000 reader. To save the result, remove the filter from the bottom end of the test strip.
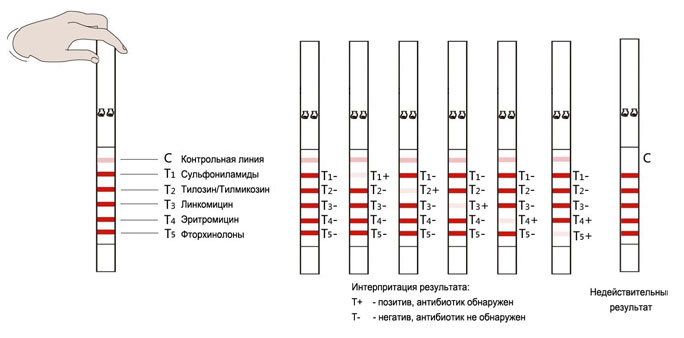
Negative result (-): control line (C) is colored red; The test line corresponding to its antibiotic (T1 ... T5) is colored brighter than the control line (C) or has the same staining intensity as the control line (C). This means that the sample contains no antibiotics at all, or contains less than the detection limit of the test kit (see Table 1).
Positive result (+): the control line (C) is colored red; the test line corresponding to its antibiotic (T1 ... T5) is absent or has a weaker staining intensity compared to the control line (C). This means that the sample contains an antibiotic corresponding to its band that is greater than the detection limit of the test kit (see Table 1).
Invalid result: control line (C) did not appear at all. This means that the analysis was not carried out correctly, or the test strip has deteriorated. The test must be repeated.
Note:
- The test kit is a qualitative method for detecting residual amounts of antibiotics in milk, whey.
- Do not use damaged or expired kit components.
- Once the kit has been taken out of the refrigerator, opened components should preferably be used within 24 hours.
- Hold the test strip by the upper end only. Do not touch the test strip filter! Do not touch the membrane in the middle of the test strip!
- Close the tube tightly after removing the required number of test strips and wells.
- Place the test strips in the wells of the working part with the filter.
- Each time a new sample is taken, take a new disposable Pasteur pipette to avoid accidental contamination.
- The test strip is used only once.
- Samples of milk and whey, the mixture of sample and dye in the well must be homogeneous. The study of milk and whey samples with foreign particles, clots and separation phases can lead to distorted results.
- If necessary, it is possible to store a test strip with a result of no more than 12 months.
- One test strip and one well with a reagent are used per sample, the remaining test strips and wells are stored in a closed tube at a temperature of 2-8 ° C.
Contents of the kit: The kit includes everything you need for 96 definitions:
- 12 tubes, each containing 1 strip with 8 wells with a reagent containing antibodies and 8 test strips;
- 100 disposable Pasteur pipettes or 100 tips (200 µl dosing pipette, optional);
- Instruction;
- 8 wells with control reagent - Positive standard (the concentration of antibiotic is indicated on the packaging of the positive control and on the quality certificate that goes with each batch of test kits);
- negative control reagent bottle (does not contain antibiotics);
- 1 well plate;
- cards with QR codes for calibrating the BMZ6000 reader (see instructions for the reader).
Sample preparation of milk and whey samples:
Powdered milk, powdered milk whey: Dissolve the sample in a suitable flask with warm distilled water (according to the current regulatory documentation), mix thoroughly.
Milk , reconstituted milk powder, reconstituted whey powder: Samples must be liquid and homogeneous. Samples should be free of clots and product separation phases. The temperature of the sample must be at least 4°C, neither frozen nor heated. Mix the sample thoroughly before testing.
Preparing the Mini-T Incubator:
The analysis can be carried out with or without an incubator.
When using an incubator, do the following: Place the incubator on a work bench with a flat surface. Connect the power supply to the incubator, and then plug it into a 220V socket. Set the switch to working position. Next, set the operating temperature to 40 ° C and wait until the device heats up. Once the incubator has reached operating temperature, the sample well can be placed in the appropriate hole.
Carrying out self-testing of the test kit:
Before you start working with samples, you should perform a self-test on the test kit. To do this, use the negative and positive controls included in the kit. Further work is permitted on a kit with validated antibiotic performance and detection limits if a negative control is completely negative and a positive control is completely positive.